U.S. to Become World’s Largest Grid-Connected Energy-Storage MarketU.S. to Become World’s Largest Grid-Connected Energy-Storage Market
Deployments of grid-connected energy storage in the United States expected to touch 712 MW, surpassing South Korea's.
May 28, 2019

By T&DWorld Staff
The United States will this year become the world’s largest market for grid-connected battery energy storage, as solar-plus-storage and peaking capacity requirements drive increased procurement, according to IHS Markit.
Deployments of grid-connected energy storage in the United States this year are expected to amount to 712 MW, almost double of 376 MW in 2018. This will help the United States surpass South Korea, where the market might drop significantly below 600 MW.
The increasing market activity in the United States is being propelled by significant regulatory and policy developments as well as the diversification in major applications and geographic activity.
U.S. Market Charges Up
The strong performance of the United States in 2019 represents a complete turnaround from 2018, when U.S. deployment stagnated and that of South Korea boomed. The year 2018 set a record for grid-connected battery energy storage as global installations nearly doubled, largely driven by the growth in South Korea in the first half of the year. However, growth in the United States was slower, with deployments increasing by only about 22%.
In 2019, several major factors have come into play to fuel U.S. growth, including:
Federal policies such as FERC Order 841 are driving regional grid operators across the country to incorporate additional market mechanisms that will enable more participation of energy-storage resources in wholesale market activities.
The investment tax credit (ITC) currently available for solar is driving the development of a rapidly growing utility-scale solar-plus-storage project pipeline, particularly in the Western United States.
State-level energy storage mandates and incentives are helping to kickstart development in progressive markets that are also wrestling with relatively high levels of renewable energy penetration.
Utilities are ramping up procurements of both behind-the-meter and front-of-the-meter energy storage resources to integrate higher levels of renewables and provide additional grid services such as demand response.
Solar-Plus-Storage to Drive U.S. Energy-Storage Market
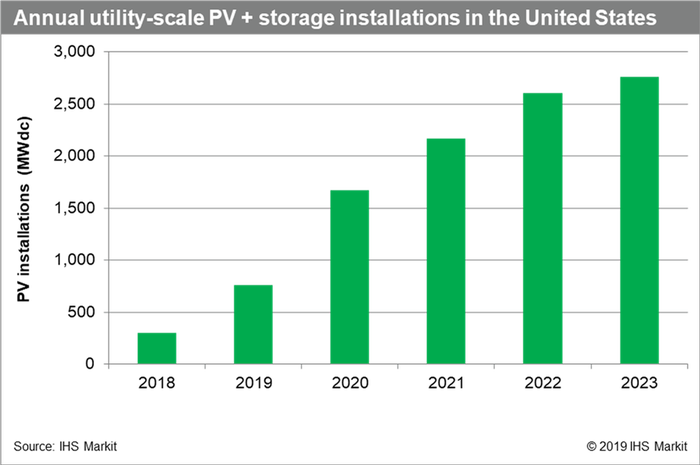
IHS Markit expects over 2 GW of energy storage to be paired with utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) systems from 2019 to 2023 in the United States. The availability of the ITC through 2023 for battery-storage systems coupled with solar PV has spurred development over the past year and will be the primary driver of co-locating utility-scale PV with energy storage. A majority of these systems are projected to be deployed in markets across the Western United States, including Hawaii, California, and Arizona, enabling further integration of PV in relatively saturated markets.
In terms of installed PV capacity, 10-GW dc of utility-scale PV installations is predicted to be paired with energy storage from 2019 to 2023, accounting for 16% of utility-scale PV installations during the period.
Cost synergies and operational efficiencies by pairing the two technologies can offer significant value, but it is overshadowed by the opportunity of reducing the capital costs of energy storage by up to 30% with the ITC.
Dc-coupled systems can have a small but significant cost advantage over ac-coupled ones depending on system size and characteristics, with the primary benefits being the reduction of power conversion equipment required and the ability-recapture dc energy otherwise clipped. While ac-coupled systems are better suited for flexibly participating in a wider array of ancillary services, both system types can leverage the ITC and benefit from shared installation and operational costs.
In terms of the 30-year levelized cost of energy (LCOE), IHS Markit estimates that adding 25 MW / 100 MWh of energy storage to a 100-MW ac single-axis tracking PV system in 2019 could increase the pre-ITC cost of energy by 35 to 40%, assuming the battery system is replaced after 15 years. After accounting for installation and operational synergies of dc-coupling and applying the ITC to the cost of both solar and energy storage, an LCOE below US$40/MWh can be achieved.
By 2023, IHS Markit forecasts solar-plus-storage to be a competitive resource compared with new natural gas resources in the United States.
You May Also Like






