New Robotic Language Inspired by Bees’ ‘Waggle Dance’
The visual language could be used in little to no-access areas, such as space or search-and-rescue missions

The ‘waggle dance’ used by bees to communicate with one another where pollen is located is the inspiration for a new motion-based robotic language.
A study published this month in Frontiers in Robotics and AI demonstrated the successful use of this unusual method of communication for robot-to-robot interaction, allowing them to communicate with one another without requiring a network connection.
Bee colonies can communicate the location of nearby flowers in both distance and direction by wiggling their behinds in the direction of the pollen source. The length of the dance indicates the distance to the source, while the direction of the dance indicates the flowers’ location.
To test this method for robotic communication, researchers from the University of Maryland and the Indian Institute of Science had two warehouse robots arrange the movement of a package interacting with only vision-based cues.
A human worker initially gave instructions to one robot using hand gestures, which the robot interpreted using cameras and skeletal tracking algorithms. This bot then passed along the details to a handling robot by tracing a symbol on the ground; with the symbol’s shape representing the direction of travel, and the time it takes to draw the shape representing the distance to the package’s destination.
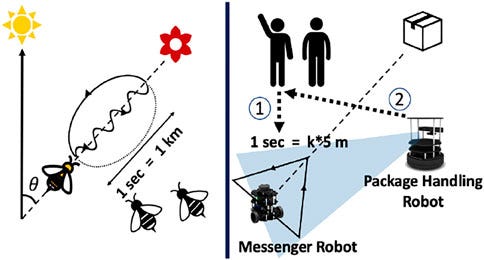
A diagram of how bees’ movements show direction and distance to pollen source.
Credit: Frontiers in Robotics and AI
This novel method was shown to have a 93.3% accuracy in simulations and a 90% accuracy in physical practice.
Such a method could be useful in remote areas where network connection is intermittent or unreliable, in search-and-rescue missions where networks are damaged or destroyed, or even in space missions where networks are not yet established.
As the technique relies solely on a simple camera, it can be deployed on any kind of robot and is both scalable and customizable, making its real-world applications limitless, according to the researchers.
Next, the team will be looking to fine-tune the method, increasing the robots’ ability to recognize different human gestures as well as the varying intensities of human gestures.
About the Author
You May Also Like








