Humanoid Robot Designed to Automate Home ChoresHumanoid Robot Designed to Automate Home Chores
1X CEO tells IoT World Today how the AI in the NEO humanoid robot AI adapts to user needs and automates their chores

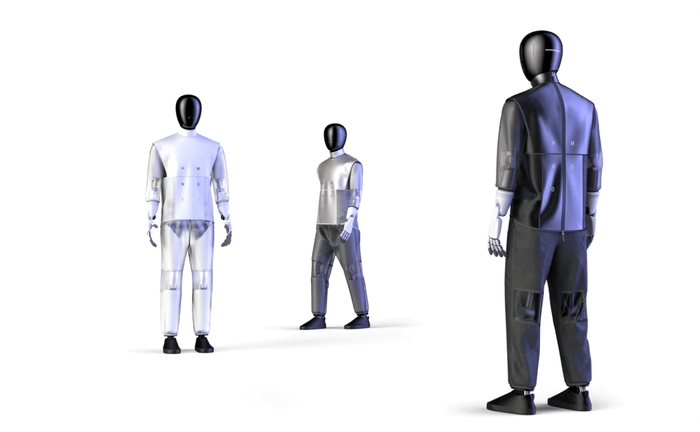
Robotics company 1X has revealed NEO, a humanoid robot designed for general-purpose tasks in homes. The lightweight NEO robot autonomously performs tasks using its built-in AI.
NEO is of average human height, 5.5 feet tall, and weighs 66 pounds, which is equivalent to the size of a Dalmatian.
Despite its lightweight design, the robot can lift double its weight (154 pounds), carry 44 pounds and run at speeds of up to 7.5 mph.
Unlike industrial humanoid robots like the ones being developed by Apptronik, 1X is looking to bring NEO to homes.
The team behind NEO highlighted the humanoid’s sophisticated AI and learning capabilities as what sets it apart from other humanoid robots.
Bernt Øivind Børnich, 1X's CEO and founder, explained to IoT World Today, "Our objective is to deliver a product that performs the tasks you prefer not to do, tailored to your specific preferences and lifestyle. This customization is not predetermined; it requires you to instruct the robot."
NEO's design centers on accessibility and safety. Unlike its predecessor EVE, which stood at 6 feet, 1 inch tall and weighed 196 pounds, NEO is lightweight, soft and compliant, engineered for safe interaction with humans in their homes.
"For me, it is essential to provide accessibility and the tools that empower our customers, alongside our operators, to automate tasks that are important to them,” Børnich said. “Imagine receiving a NEO robot at home; the first thing it communicates is, 'Hi I'm NEO. I am here to help you complete whatever tasks you desire.’ This level of personalization is crucial because everyone's needs are unique.”

Credit: 1X Technologies
1X wants NEO to perform routine chores such as cleaning and organizing. The robot leverages learnings from 1X’s prior EVE robot, which the company used as a training platform to improve the underlying AI that powers NEO.
Humanoids aren’t a new concept in robotics. Honda’s ASIMO, for example, could perform several menial tasks like carrying drinks and that was developed in the early 2000s.
Børnich told IoT World Today that ASIMO failed due to issues with dynamics and energy with NEO possibly thanks to advances in AI.
"What people underestimate is you need to be able to scale this,” he said. “It has to do a lot with the dynamics in the hardware of how we move in our surroundings and the energy in these systems like stiff versus more modern bio-inspired robotics."
NEO can run for two hours and uses little energy due to onboard motors which generate force at about 80% of the force density of human muscle — without the need for gears.
The robot also doesn’t rely on classical stiff actuators, instead leveraging more flexible components that allow for more fluid movements.
NEO is designed to be used out of the box and the more it’s used, the smarter it gets.
Domestic use will enable NEO to gather data, helping build general AI models to improve the robot's systems over time.
"We're trying to solve intelligence through embodiment. And that diversity in data is the secret intelligence,” Børnich said. “It's not so secret, but it's hard to do in the real world if you don't have a safe and dynamic robot."
1X (formerly Halodi Robotics) operates in the U.S. and Norway and was previously backed by ChatGPT maker OpenAI.
About the Author
You May Also Like
.jpg?width=100&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.jpg?width=400&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)