Connects decision-makers and solutions creators to what's next in quantum computing
Mobile Quantum Computer Planned for 2027; World FirstMobile Quantum Computer Planned for 2027; World First
Four quantum startups intend to miniaturize quantum technology for defense, security and civilian use

Germany's Cyber Agency Agentur Cyberagentur has awarded Quantum Brilliance, ParityQC, Oxford Ionics and NeQxt contracts to develop the world’s first mobile quantum computer by 2027.
The project aims to produce a small form-factor quantum computer for defense, security and civilian applications. The companies won bids worth $39 million in funding, the largest research grant Cyberagentur has awarded.
Each company brings unique strengths to the program.
Quantum Brilliance specializes in miniaturized, room-temperature quantum chips, which rely on nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in synthetic diamonds as qubits. These chips are compatible with traditional semiconductors and provide the foundation for mobile quantum technology.
ParityQC is developing a scalable quantum architecture and operating system, ParityOS, which enables larger algorithms to be processed more efficiently and with a lower error rate.
“The potential of a quantum mobile computer is enormous for defense and cybersecurity in Germany and allied nations,” said Quantum Brilliance CEO Mark Luo.
ParityQC co-CEOs Wolfgang Lechner and Magdalena Hauser added: “We believe that the partnership with Quantum Brilliance puts us on a path to developing the world’s first mobile quantum computer.”
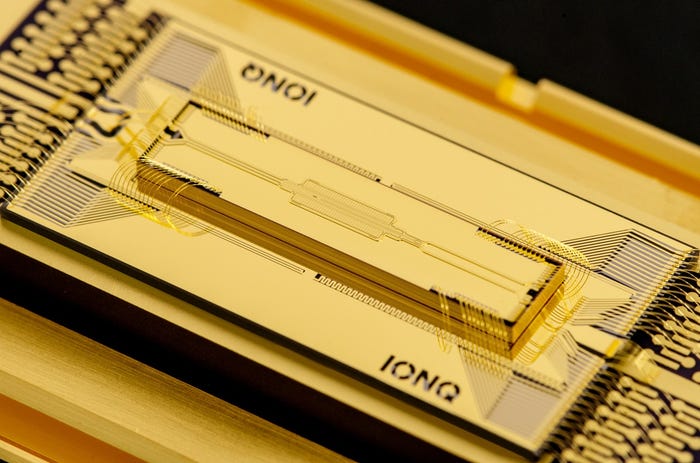
Oxford Ionics intends to develop a portable quantum computer called MinIon using its propoertary electronic qubit control technology that uses electronics, not lasers, to control its qubits. This inherently robust technology can then be integrated onto a standard, thumbnail-sized chip produced in today’s semiconductor fabrication facilities.
Dr Chris Ballance, Oxford Ionics co-founder and CEO, said: “This approach has yielded both the highest performing chips in the world and a robust technology that can deliver industry-leading performance within a small physical footprint based on customer needs. MinIon represents the first of these small systems, which is uniquely engineered to suit the dynamic, fast-paced nature of national security and defense.”
German startup neQxt aims to integrate its existing trapped-ion technology into a compact, modular, scalable and mobile system called MaQue.
The potential defense and national security applications include optimizing troop movements, analyzing battlefield scenarios and simulating biological threats in real time, even in remote locations.
Unlike traditional quantum computing solutions, it would not require cloud access to data centers, ensuring security in combat scenarios.
As the development progresses, mobile quantum computing technology could have broader applications across industries like finance, supply chain management and scientific research.
About the Author
You May Also Like